Determining which USDA plant hardiness zone you live in is essential for any gardener looking to ensure their plants thrive. The USDA zones are delineated by the average annual minimum winter temperature and serve as a guide to select perennial plants suitable for your climate. Knowing your specific zone can make a significant difference in the success of your garden, as it affects the types of plants you can grow, when to plant them, and the care they need to survive winter conditions.
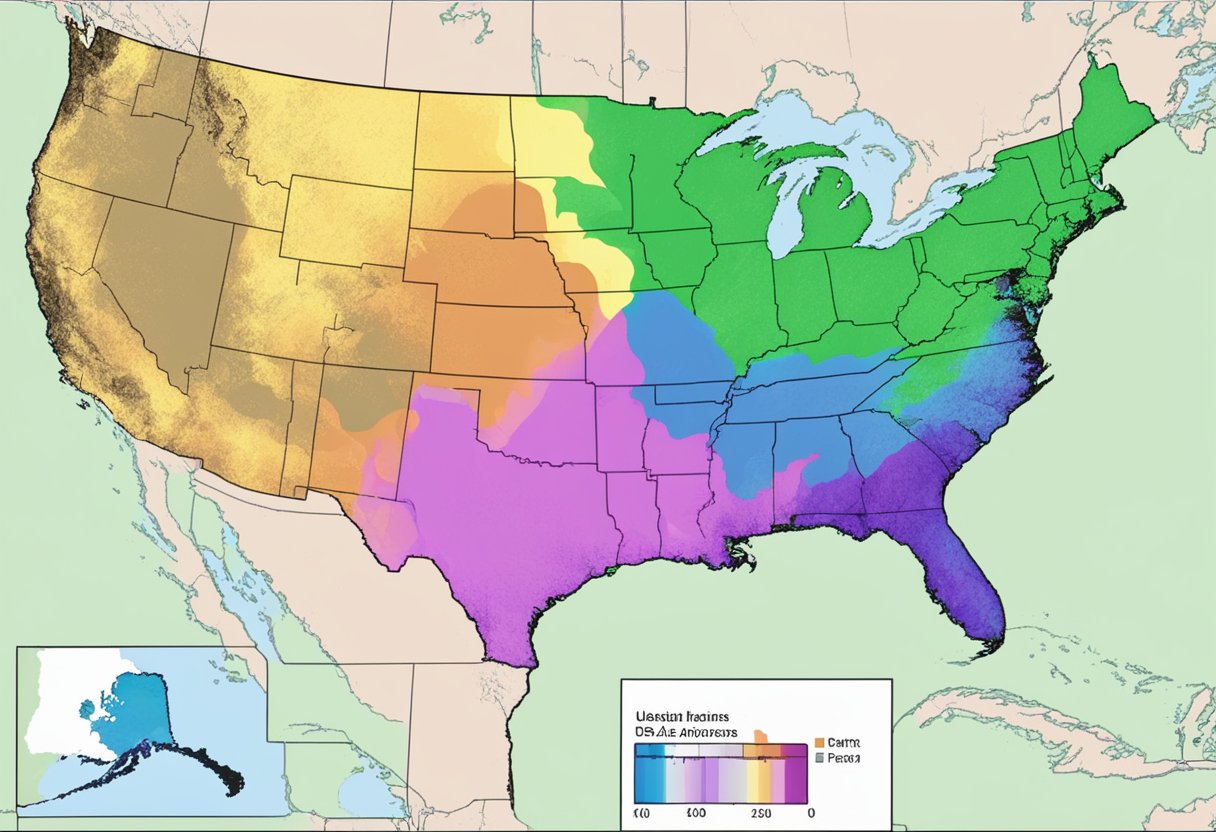
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map divides North America into 13 primary zones. Each zone is 10 degrees Fahrenheit warmer (or colder) in an average winter than the adjacent zone. If you’re looking to plant a garden, it’s important to consult this map first. The map is regularly updated to reflect the latest climate data, and using tools such as zip code lookup or interactive GIS-based maps can quickly inform you of your hardiness zone.
It’s reassuring to know that with this information, I can make informed decisions about planting. Whether I’m planning to introduce new plants to my garden or trying to figure out which plants are likely to survive the winter, understanding my USDA zone is the key to creating a robust and beautiful garden year-round.
JUMP TO TOPIC
What USDA Zone Do I Live In?
To determine your USDA plant hardiness zone, refer to the official USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, which divides North America into 13 zones based on the average annual extreme minimum temperature.
The Basics of Plant Hardiness Zones
I understand that finding your USDA plant hardiness zone is essential for garden planning. These zones are defined by the average annual extreme minimum temperature and are divided into increments of 10 degrees Fahrenheit. The hardiness zone can guide you on what plants will likely survive the winter in your area.
Interpreting the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
Interpreting the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is straightforward. Each zone on the map is numbered and colored differently, making it easy to locate your specific area. The 2023 map offers an accurate tool to match plants to your local climate, considering factors such as elevation and microclimates.
Updates to the Plant Hardiness Zone Map
I’ve observed that the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is periodically updated to reflect changing climate patterns. The most recent revision in 2023 takes into account new temperature data. It’s recommended you check the map after significant updates to ensure the information remains relevant to your gardening needs.
Factors Affecting Plant Growth and Survival
Understanding the factors that contribute to plant growth and survival is crucial for successful gardening and agriculture. These factors include the prevailing climate, soil type, and microclimates, all of which impact the hardiness of the plants in a specific USDA zone.
Climate Influence on Planting Zones
The climate in a given location heavily influences which plants can grow and survive there. The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map categorizes regions based on their average annual extreme minimum winter temperature to guide gardeners and growers. For instance, knowing whether I live in zone 6b or 7a can significantly affect the types of perennial plants I choose. Zones are defined by 10°F main divisions with finer 5°F sub-zones indicated by “a” and “b” to provide more specific guidance.
💥 Climate: Includes winter temperature, heat, and humidity levels that plants need to withstand.
Soil and Microclimate Considerations
Soil composition and microclimates also play a vital role in a plant’s success beyond just hardiness zones. My experience tells me that even within the same zone, a plant may thrive in one location and not another due to soil fertility, pH levels, and drainage properties. Specific spots around my home, like sheltered areas near walls or depressions in the landscape, can create microclimates with unique temperature and humidity profiles. This can be advantageous or detrimental to plant survival.
- Soil: Impacts nutrient availability and water retention.
- Microclimate: Caused by local geography or structures, affecting temperature and sunlight exposure.
Practical Gardening Tips Using Hardiness Zones
Understanding your USDA hardiness zone can dramatically improve your gardening success by helping you choose the right plants and adjust your gardening techniques to local climate conditions.
Selecting the Right Plants for Your Zone
When I pick plants, I always consider the zone suitability to ensure that perennials, shrubs, trees, and flowers will survive the annual extreme minimum winter temperature. Here’s a strategy I find useful:
- Zone 3: Russian Sage, Peonies
- Zone 5: Daylilies, Hostas
- Zone 7: Gardenias, Evergreen Clematis
I match my selections with the zone details from the updated USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map to make well-informed decisions that lead to flourishing gardens.
Adapting Garden Practices to Your Climate
Adjusting gardening practices to the climate associated with my hardiness zone has made a marked difference in achieving a successful garden. For instance, knowing the right time to plant is crucial. I’ve compiled a table illustrating how I adapt:
| Zone | Planting Season Start | Frost Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | Late Spring | Prepare for late frosts |
| 5 | Mid-Spring | Monitor soil temperature |
| 7 | Early Spring | Less risk of frost damage |
By adhering to climate-specific garden practices, like mulching before a freeze or watering adequately during dry spells, I increase my garden’s resilience and productivity.
Leveraging Resources and Tools for Gardeners
I live in USDA Plant Hardiness Zone 9a.
Identifying your USDA Plant Hardiness Zone is pivotal for successful gardening. With a reliable broadband internet connection, I access the USDA zone map, an indispensable tool crafted by scientists from the Agricultural Research Service.
💥 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
Using detailed, interactive GIS-based maps on the USDA website, I conveniently pinpoint my specific zone, which informs me about the garden varieties best suited to my location’s climate.
- Interactive Map: For precise determination down to half-mile square resolution.
- Update Notifications: Sign up options to receive the latest updates and advancements.
- Detailed Information: Zone specifics and microclimate considerations.
Regular updates refine the map detail, mirroring shifting climate patterns. Such attention to detail ensures that the map remains a current and an accurate guide. Lastly, I emphasize the importance of recognizing microclimates within your zone; they can significantly affect plant viability.












